Chuangde Fm
Type Locality and Naming
Himalayan North Belt. Wu Haoruo erected the Chuangde Formation in 1987. The section for the designation is in the Chuangde Village about 15 km northeast of the town of Gyangze. The reddish strata studied were referred to the Zongzhuo Fm by Yang Zunyi and Wu Shunbao (1964). Wu Haoruo (1987) described the Chuangde Formation as a set of multicolor beds in the Gyangze region. Li Xianghui et al (1999) redefined the Chuangde Formation in Gyangze by restricting the red beds as a new stratigraphic unit. Wan Xiaoqiao et al (2005) described these beds in more detail and recognized five foraminifera zones from the Chuangde Formation.
Figure: Type section of Chuangde Formation in Chuangde Village of Gyangze]
Lithology and Thickness
Flysch. The Upper Cretaceous to ?Paleocene Chuangde Formation is composed of muddy and sandy clastic turbidites with exotic or slumping blocks of different ages, particularly large amount of red boulders in different lithology and different size occur in this formation (Wan et al., 2005).
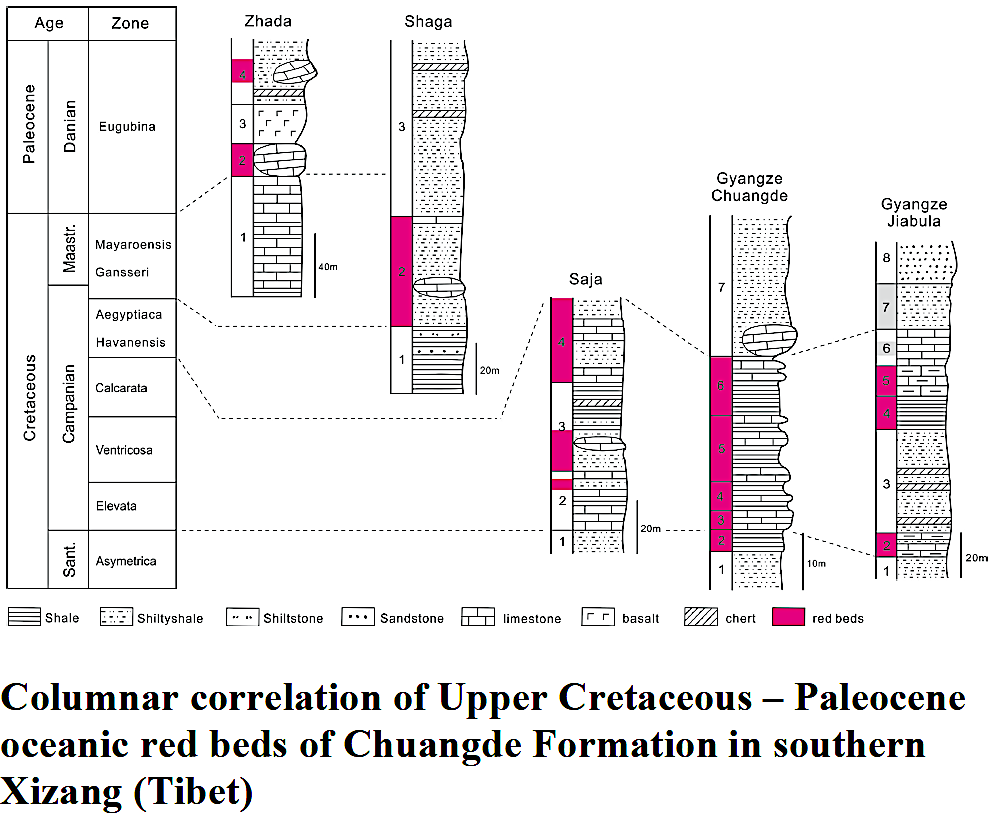
Figure: Columnar correlation of Upper Cretaceous – Paleocene oceanic red beds of Chuangde Formation in southern Xizang (Tibet)]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
The Chuangde Formation underlies the Paleogene Chaqiela Fm (previous interpretation); next higher regional unit is Zongzhou Fm of latest Cretaceous (revised interpretation by Xi et al., 2019).
Upper contact
The Chuangde Formation overlies the Jiabula Fm (according to revised strat column by Dangpeng Xi, Xiaoqiao Wan et al. (2019, China Integrated Strat))
Regional extent
The oceanic red beds are deep marine sediments deposited under pelagic oxic conditions. They are widespread in southern Xizang (Tibet), south of the Indus-Yarlung Zangbo suture. The red sequences, and the strata in southern Xizang (Tibet) tend to be younger from east to west, and indicates that the Chuangde formation in the north sedimentary sub-belt is late Santonian to Paleocene in age. (Wan et al, 2007).
GeoJSON
Fossils
As a typical locality, the oceanic red beds in the Chuangde Section span an age from the late Santonian to the middle Campanian, and consist of the Dicarinella asymetrica, Globotruncanita elevata, Globotruncana ventricosa and Globotruncanita calcarata planktonic foraminifera zones. Westward near Sagya, the red beds in the Saiqu section consist of Globotruncanita elevata, Globotruncana ventricosa and G. inneiana planktonic foraminifera, and are of Campanian age. Farther west in the Saga-Gyirong region, an abundant planktonic foraminifera fauna was described from these red beds. The age of the microfauna is Maastrichtian and is correlated with Gansserina gansseri and Abthomphalus mayaroensis zones. In the Zanda region of the westernmost Xizang (Tibet), the Longji section yields a large amount of planktonic foraminifera. They are referred to the Globigerina eugubina-G. fringa fauna of the early Paleocene.
Age
Depositional setting
The oceanic red beds are deep marine sediments deposited under pelagic oxic conditions.
Additional Information